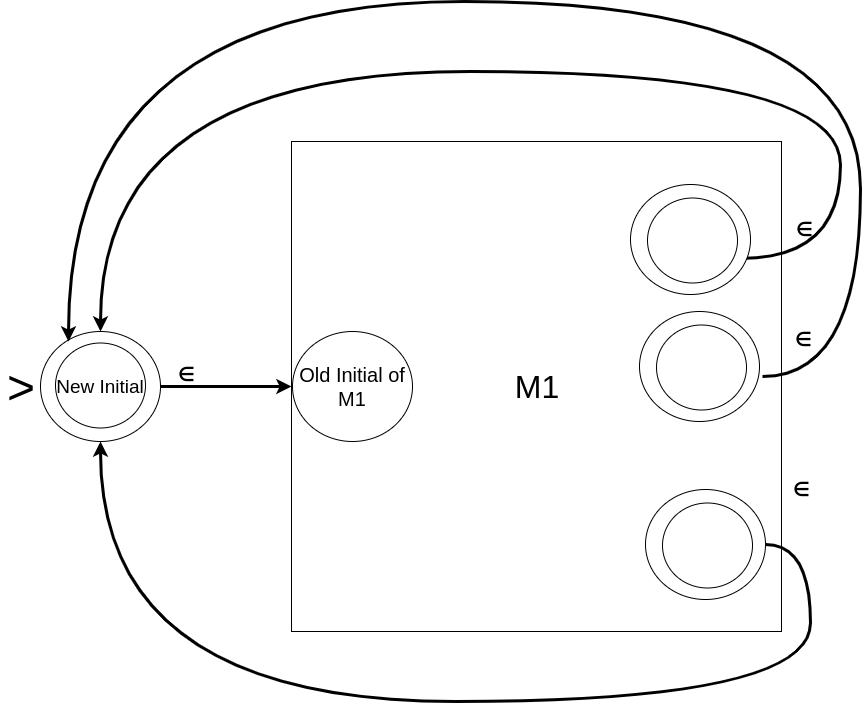
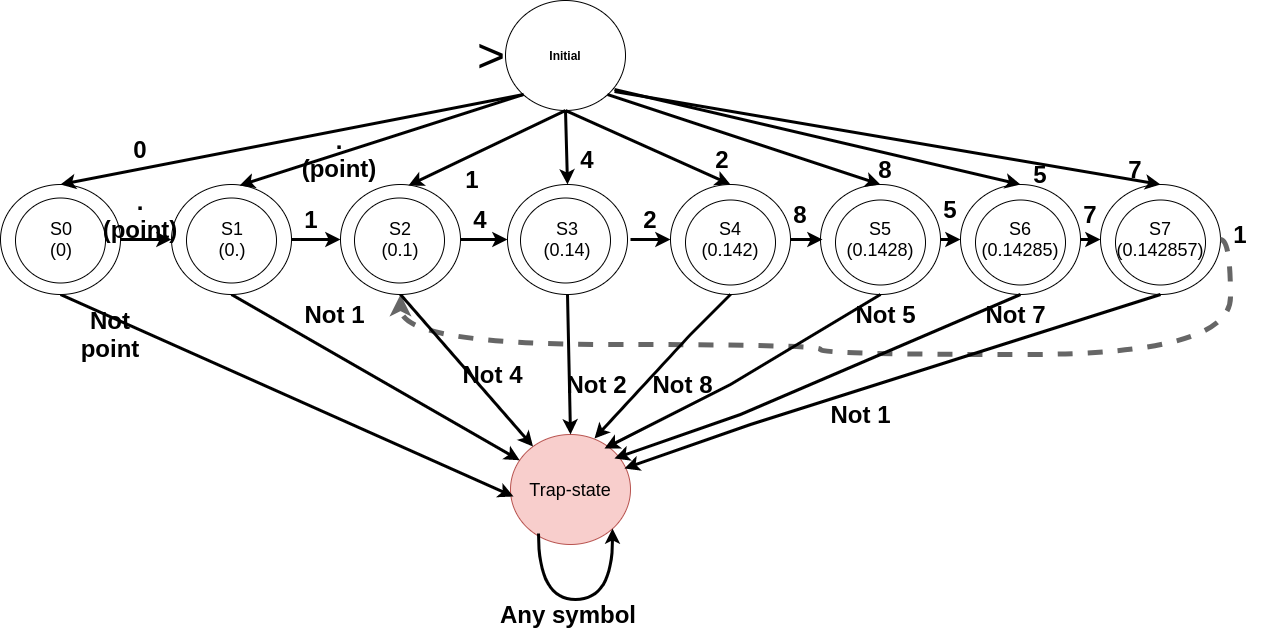
Again, this post is meant specifically for undergraduate students (first timers into automata theory) – a very brief introduction of FSA: Finite State Automaton (Automata when plural). This post is the third of four parts: the first part covers an elementary introduction to FSA and DFA (Deterministic Finite Automaton), the second part encompasses some common examples illustrating…
Category: Algorithm Design and Analysis
FSA Part III: Concoction of design-strategies
Again, this post is meant specifically for undergraduate students (first timers into the automata theory) – a very brief introduction of FSA: Finite State Automaton (Automata when plural). This post is the third of four parts: the first part covers an elementary introduction to FSA and DFA (Deterministic Finite Automaton), the second part encompasses some common examples…
FSA Part II: Concoction of design-strategies
Again, this post is meant specifically for the undergraduate students (the first timers into the automata theory) – a very brief introduction of FSA: Finite State Automaton (Automata when plural). This post is the second of the four parts: the first part covers an elementary introduction to FSA and DFA (Deterministic Finite Automaton), this part encompasses some…
FSA Part I: An elementary introduction
Again, this post is meant specifically for the undergraduate students (the first timers into the automata theory) – a very brief introduction of FSA: Finite State Automaton (Automata when plural). This post is in four parts: this part covers an elementary introductions to FSA and DFA (Deterministic Finite Automaton), Part II encompasses some common examples illustrating…
Algorithmic Time-Complexity Analysis: Asymptotic Notation
Motivation: When we talk about efficiency of an algorithm, we generally refer to the resources (time, space etc.) that the algorithm will consume for a given input. Especially, we usually are interested in how an algorithm will behave (as in how much time or space will be consumed) for voluminous input size. A solution to predict the behaviour (say…
Algorithm to find the Least Lexicographic Rotation of a circular string
Background: A string is a sequence of symbols from a set called an alphabet. If the string is circular, one can start reading it from any position/index. For example, consider the following circular string of length 8: If we read this circular string starting at 12 o’clock position and moving in clockwise direction, we obtain”abaabbab“….